By Fadi Maalouf, Chief Technology Officer, Dii Desert Energy
Energy storage is emerging as a cornerstone in the global transition to net zero, particularly in regions like the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) where renewable energy potential is vast. The ability to store and manage energy generated from sources like solar and wind is vital for ensuring reliability, balancing demand, and reducing dependency on fossil fuels. In the MENA region, technologies such as Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), Thermal Energy Storage Systems (TESS), and Pumped Hydro Energy Storage Systems (PHES) are playing increasingly significant roles in shaping the future energy landscape.
Background: The Importance of Energy Storage
The energy transition to net zero is rooted in decarbonizing electricity production while meeting growing energy demands. Renewable energy sources, though abundant, are inherently intermittent; solar power fluctuates with daylight hours, and wind energy varies with meteorological conditions. This intermittency poses challenges for maintaining grid stability and ensuring uninterrupted energy supply, especially in regions with extreme temperatures and high electricity demands like MENA.
Energy storage systems serve as a bridge to overcoming these challenges. By capturing surplus energy during peak generation times and releasing it during high demand or low generation periods, storage technologies enable a smoother integration of renewables into the energy mix. Moreover, they provide critical ancillary services such as frequency regulation and voltage control, further enhancing grid resilience. In the broader pursuit of net zero, energy storage is essential for reducing reliance on fossil fuel backup systems and maximizing the utilization of clean energy
Current Status of Energy Storage in MENA
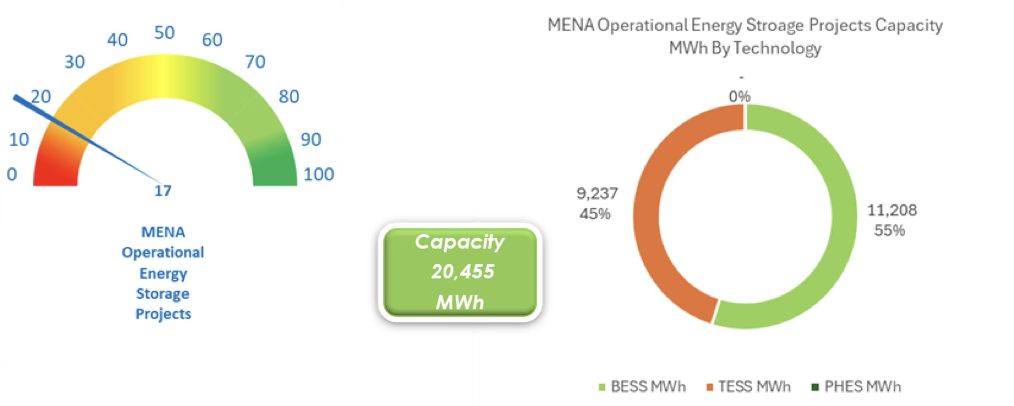
To investigate the matter, we can adopt the generic yet powerful approach: “follow the money”. In this case for MENA energy storage, we implement a direct straightforward approach: “show me the data”. Based on Dii’s MENA Energy Storage Database (Figure 1), there is a total of 17 operational utility scale renewable energy storage projects in MENA, and their total capacity is 20,455 MWh. BESS is the dominant technology with around 55% share of total capacity. TESS capacity is second at 45% and is primarily thermal storage that is coupled with CSP plants in UAE, Kuwait and Morocco.
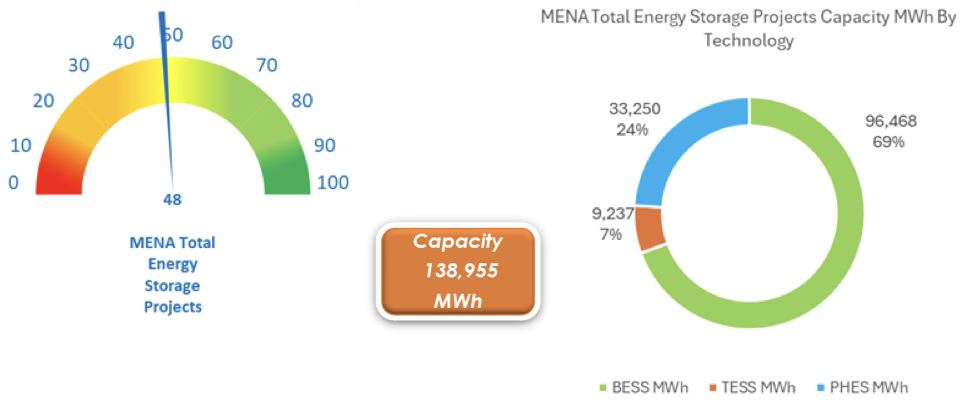
For the medium-term horizon, by 2030 or so, MENA energy storage project data paints an exponential growth picture, approximately 7-fold increase (Figure 2). There is a total of 48 utility scale renewable energy storage projects that are expected to be operational in MENA. These 48 projects have a total capacity of 138,955 MWh. BESS is the dominant technology with around 69% share of total capacity. PHES has significant potential by 2030+. At present, no new TESS developments for are forecasted.
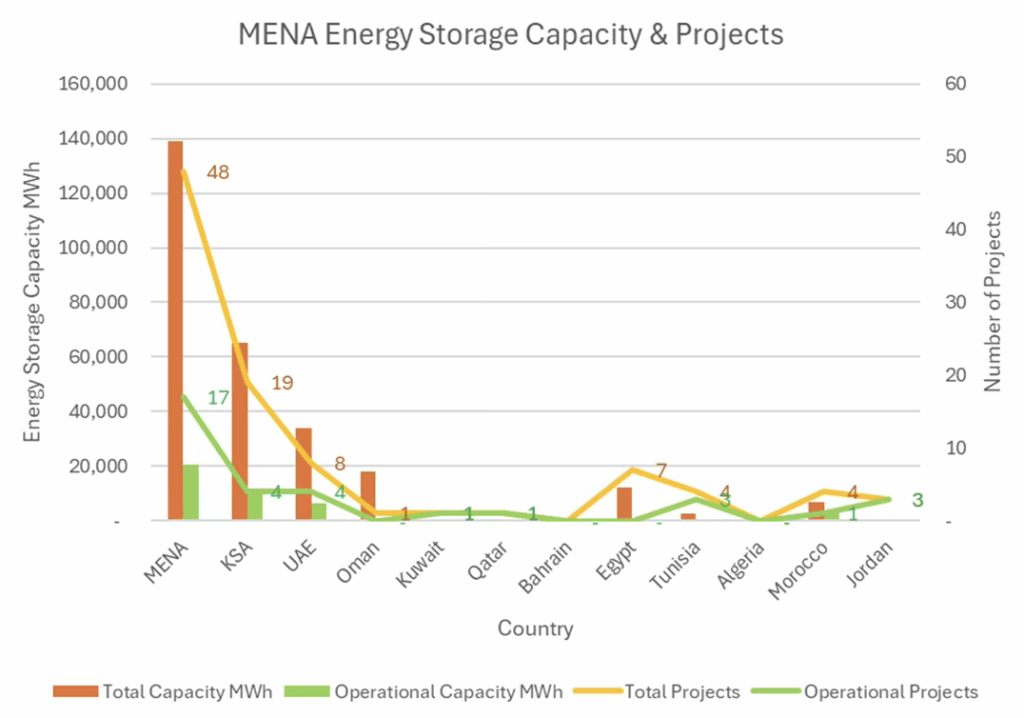
Analyzing the data further (Figure 3), we conclude that the GCC is leading in developing energy storage projects and capacity. KSA and UAE are at the forefront. By 2030, we expect that north African countries will pick up the pace of energy storage project development. We believe that Egypt and Morocco will be leading in north Africa.
Outlook for Energy Storage in MENA
The transition to net zero in MENA is gaining momentum with ambitious renewable energy targets set by countries like Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman, Egypt and Morocco. Energy storage technologies will play a pivotal role in achieving these goals by enabling a reliable and sustainable energy supply. Investments in research and development, coupled with supportive policies and international collaboration, are needed to overcome existing barriers and unlock the full potential of BESS, TESS, and PHES.
Emerging trends such as hybrid storage solutions and advances in artificial intelligence for energy management promise to further enhance the efficiency and adaptability of storage systems. By embracing these innovations, MENA can position itself as a global leader in renewable energy and storage technologies.
Energy storage is not just a complement to renewable energy; it is an enabler of the profound transformation required to achieve net zero. In MENA, the advancement BESS, TESS, and PHES reflects the region’s commitment to sustainability and energy resilience. As investments continue to flow and technologies evolve, energy storage will undoubtedly serve as the cornerstone of the MENA energy transition, paving the way for a cleaner, brighter future. So yes, it’s a Boom!